Mixed Models
Last Updated: 22, November, 2022 at 09:24
- 100 populations of penguins
- Pre and Post Penguins
- Three repeated measures
- Interaction effects
- Real data (cars)
- Vik 2013, Chapter 18 (Repeated measures ANOVA)
library(tidyverse)
## ── Attaching packages ─────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.2 ──
## ✔ ggplot2 3.4.0 ✔ purrr 0.3.5
## ✔ tibble 3.1.8 ✔ dplyr 1.0.10
## ✔ tidyr 1.2.1 ✔ stringr 1.4.1
## ✔ readr 2.1.3 ✔ forcats 0.5.2
## ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
## ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
100 populations of penguins
Make data
sample_size <- 15
populations <- 100
variance_random_effect <- 0.25
fixed_effect <- 2.5
random_factor <- rnorm(populations, 0, sd=sqrt(variance_random_effect))
all_heights <-c()
all_weights <-c()
all_ids <-c()
for (i in 1:populations){
heights <- rnorm(sample_size)
errors <- rnorm(sample_size, sd=0.25)
weights <- fixed_effect * heights + random_factor[i] + errors
population_ids <- rep(i, times = sample_size)
all_heights <- c(all_heights, heights)
all_weights <- c(all_weights, weights)
all_ids <- c(all_ids, population_ids)
}
penguin_data <- data.frame(all_ids, all_heights, all_weights)
colnames(penguin_data) <-c('id', 'height', 'weight')
head(penguin_data)
## id height weight
## 1 1 1.0132414 3.05601620
## 2 1 -0.1961190 0.40011681
## 3 1 1.1605701 3.11715018
## 4 1 1.4982667 3.86164382
## 5 1 -0.1847411 -0.02184106
## 6 1 0.2838344 0.99680182
Fit a mixed model
v <- var(random_factor)
s <- sd(random_factor)
c(v, s)
## [1] 0.3173358 0.5633256
fitting the model using the lme function
The 1 indicates that an intercept is to be fitted for each level of the random variable.
library(nlme)
##
## Attaching package: 'nlme'
## The following object is masked from 'package:dplyr':
##
## collapse
model <- lme(weight ~ height, random=~1|id, data = penguin_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed-effects model fit by REML
## Data: penguin_data
## AIC BIC logLik
## 621.7874 643.0349 -306.8937
##
## Random effects:
## Formula: ~1 | id
## (Intercept) Residual
## StdDev: 0.5618467 0.2564819
##
## Fixed effects: weight ~ height
## Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
## (Intercept) -0.0486186 0.05657444 1399 -0.8594 0.3903
## height 2.4911404 0.00682139 1399 365.1954 0.0000
## Correlation:
## (Intr)
## height 0.005
##
## Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
## Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
## -3.05759231 -0.65677281 0.01564323 0.64320305 3.11810783
##
## Number of Observations: 1500
## Number of Groups: 100
Intepreting the fitted parameters
A different intercept is fitted for each population.
coefs <-coefficients(model)
coefs$population <- seq(1, populations)
head(coefs, 15)
## (Intercept) height population
## 1 0.526867568 2.49114 1
## 2 -0.767752577 2.49114 2
## 3 -0.423889557 2.49114 3
## 4 0.095871919 2.49114 4
## 5 0.192433362 2.49114 5
## 6 1.101717851 2.49114 6
## 7 0.465020067 2.49114 7
## 8 0.200583753 2.49114 8
## 9 0.109259152 2.49114 9
## 10 -0.388478756 2.49114 10
## 11 -0.823064720 2.49114 11
## 12 -0.475840389 2.49114 12
## 13 0.687135151 2.49114 13
## 14 0.546711903 2.49114 14
## 15 -0.009223082 2.49114 15
head(penguin_data)
## id height weight
## 1 1 1.0132414 3.05601620
## 2 1 -0.1961190 0.40011681
## 3 1 1.1605701 3.11715018
## 4 1 1.4982667 3.86164382
## 5 1 -0.1847411 -0.02184106
## 6 1 0.2838344 0.99680182
population1<-filter(penguin_data, id==1)
population2<-filter(penguin_data, id==2)
population3<-filter(penguin_data, id==3)
prediction1 <- coefs$`(Intercept)`[1] + coefs$height[1] * population1$height
prediction2 <- coefs$`(Intercept)`[2] + coefs$height[2] * population2$height
prediction3 <- coefs$`(Intercept)`[3] + coefs$height[3] * population3$height
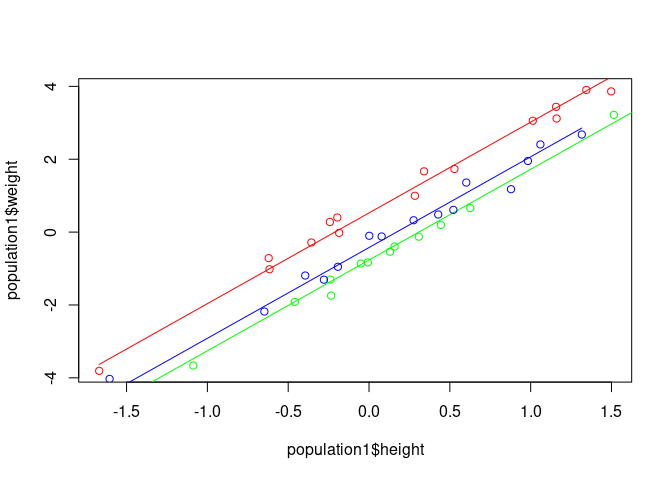
plot(population1$height, population1$weight, col='red')
points(population1$height, prediction1, type='l', col='red')
points(population2$height, population2$weight, col='green')
points(population2$height, prediction2, type='l', col='green')
points(population3$height, population3$weight, col='blue')
points(population3$height, prediction3, type='l', col='blue')
fitting the model using the lmer function
library(lme4)
## Loading required package: Matrix
##
## Attaching package: 'Matrix'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:tidyr':
##
## expand, pack, unpack
##
## Attaching package: 'lme4'
## The following object is masked from 'package:nlme':
##
## lmList
model <- lmer(weight ~ height + (1|id), data = penguin_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
## Formula: weight ~ height + (1 | id)
## Data: penguin_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 613.8
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -3.05759 -0.65677 0.01564 0.64320 3.11811
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## id (Intercept) 0.31567 0.5618
## Residual 0.06578 0.2565
## Number of obs: 1500, groups: id, 100
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error t value
## (Intercept) -0.048619 0.056574 -0.859
## height 2.491140 0.006821 365.195
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr)
## height 0.005
library(lmerTest)
##
## Attaching package: 'lmerTest'
## The following object is masked from 'package:lme4':
##
## lmer
## The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
##
## step
# To get (estimated) degrees of freedom and the p -values associated with the t -statistics and those degrees of freedom
model <- lmer(weight ~ height + (1|id), data = penguin_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [
## lmerModLmerTest]
## Formula: weight ~ height + (1 | id)
## Data: penguin_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 613.8
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -3.05759 -0.65677 0.01564 0.64320 3.11811
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## id (Intercept) 0.31567 0.5618
## Residual 0.06578 0.2565
## Number of obs: 1500, groups: id, 100
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -4.862e-02 5.657e-02 9.900e+01 -0.859 0.392
## height 2.491e+00 6.821e-03 1.402e+03 365.195 <2e-16 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr)
## height 0.005
Pre and Post Penguins
Make data
sample_size <- 100
variance_random_effect <- 0.25
fixed_effect <- 0.5
random_factor <- rnorm(populations, 0, sd=sqrt(variance_random_effect))
noise <- rnorm(populations, 0, sd=0.1)
ids <- seq(sample_size)
pre_data <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + random_factor + noise
post_data <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10 + fixed_effect) + random_factor + noise
id <- c(ids, ids)
measurement<-c(rep(1, sample_size), rep(2, sample_size))
weight <-c(pre_data, post_data)
repeated_data <- data.frame(id, measurement, weight)
repeated_data$measurement <- as.factor(repeated_data$measurement)
head(repeated_data)
## id measurement weight
## 1 1 1 9.891087
## 2 2 1 8.779557
## 3 3 1 9.275041
## 4 4 1 9.806396
## 5 5 1 11.578583
## 6 6 1 9.501858
v <- var(random_factor)
s <- sd(random_factor)
c(v, s)
## [1] 0.1918788 0.4380397
Fit model
library(lme4)
model <- lmer(weight ~ measurement + (1|id), data = repeated_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [
## lmerModLmerTest]
## Formula: weight ~ measurement + (1 | id)
## Data: repeated_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 583
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.32352 -0.55351 -0.02272 0.45857 2.61415
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## id (Intercept) 0.2561 0.5061
## Residual 0.8365 0.9146
## Number of obs: 200, groups: id, 100
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 10.2303 0.1045 187.6877 97.874 < 2e-16 ***
## measurement2 0.3498 0.1293 99.0000 2.704 0.00806 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr)
## measuremnt2 -0.619
Intepreting the model
It turns out that getting the variance terms is a bit tricky:
- https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/122218/why-do-the-estimated-values-from-a-best-linear-unbiased-predictor-blup-differ
- https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_variance.html#ref-usage
library(insight)
get_variance_random(model)
## var.random
## 0.256094
get_variance_intercept(model)
## var.intercept.id
## 0.256094
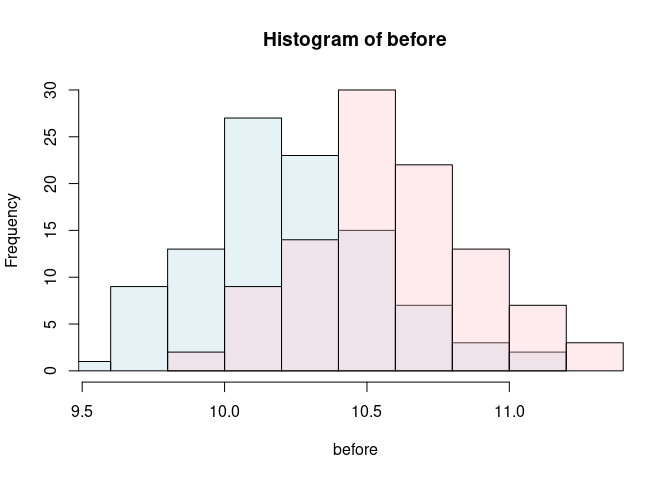
predictions <-unname(predict(model))
before <- predictions[1: sample_size]
after <- predictions[101:length(predictions)]
c1 <- rgb(173,216,230,max = 255, alpha = 80, names = "lt.blue")
c2 <- rgb(255,192,203, max = 255, alpha = 80, names = "lt.pink")
hist(before, col=c1, xlim=range(predictions), ylim=c(0, 30))
hist(after, add=TRUE, col=c2)
Three repeated measures
sample_size <- 100
variance_random_effect <- 0.25
time_effect1 <- 0.75
time_effect2 <- 1
random_factor <- rnorm(populations, 0, sd=sqrt(variance_random_effect))
ids <- seq(sample_size)
data1 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + 0.0000000000 + random_factor
data2 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + time_effect1 + random_factor
data3 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + time_effect2 + random_factor
id <- c(ids, ids, ids)
measurement<-c(rep(1, sample_size), rep(2, sample_size), rep(3, sample_size))
weight <-c(data1, data2, data3)
three_repeats_data <- data.frame(id, measurement, weight)
three_repeats_data$measurement <- as.factor(three_repeats_data$measurement)
head(three_repeats_data)
## id measurement weight
## 1 1 1 10.996181
## 2 2 1 8.874400
## 3 3 1 9.928699
## 4 4 1 9.636390
## 5 5 1 9.992006
## 6 6 1 10.053005
v <- var(random_factor)
s <- sd(random_factor)
c(v, s)
## [1] 0.2401001 0.4900001
library(lme4)
model <- lmer(weight ~ measurement + (1|id), data = three_repeats_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [
## lmerModLmerTest]
## Formula: weight ~ measurement + (1 | id)
## Data: three_repeats_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 904.5
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -3.2276 -0.6114 -0.0191 0.5081 2.8819
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## id (Intercept) 0.1981 0.4451
## Residual 1.0063 1.0031
## Number of obs: 300, groups: id, 100
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 9.9992 0.1097 281.7526 91.114 < 2e-16 ***
## measurement2 0.7905 0.1419 198.0000 5.572 8.15e-08 ***
## measurement3 0.8718 0.1419 198.0000 6.145 4.31e-09 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr) msrmn2
## measuremnt2 -0.646
## measuremnt3 -0.646 0.500
Interaction effects
sample_size <- 100
variance_random_effect <- 0.25
random_factor <- rnorm(populations, 0, sd=sqrt(variance_random_effect))
sex <- c(rep(0, sample_size/2), rep(1, sample_size/2))
ids <- seq(sample_size)
data1 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + 0 + sex * 0 + random_factor
data2 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + 1 + sex * 2 + random_factor
data3 <- rnorm(sample_size, mean = 10) + 2 + sex * 4 + random_factor
id <- c(ids, ids, ids)
sex <-c(sex, sex, sex)
measurement<-c(rep(0, sample_size), rep(1, sample_size), rep(2, sample_size))
weight <-c(data1, data2, data3)
interaction_data <- data.frame(id, measurement, sex, weight)
interaction_data$measurement <- as.factor(interaction_data$measurement)
interaction_data$sex <- as.factor(interaction_data$sex)
head(interaction_data)
## id measurement sex weight
## 1 1 0 0 10.056124
## 2 2 0 0 10.116942
## 3 3 0 0 9.712168
## 4 4 0 0 9.199921
## 5 5 0 0 9.932677
## 6 6 0 0 10.364047
v <- var(random_factor)
s <- sd(random_factor)
c(v, s)
## [1] 0.2215383 0.4706785
library(lme4)
model <- lmer(weight ~ measurement * sex + (1|id), data = interaction_data)
summary(model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [
## lmerModLmerTest]
## Formula: weight ~ measurement * sex + (1 | id)
## Data: interaction_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 903.3
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.17388 -0.66227 -0.06505 0.63431 2.71681
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## id (Intercept) 0.1972 0.4441
## Residual 0.9996 0.9998
## Number of obs: 300, groups: id, 100
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 10.2115 0.1547 278.8570 66.001 < 2e-16 ***
## measurement1 1.1233 0.2000 196.0000 5.617 6.58e-08 ***
## measurement2 1.8399 0.2000 196.0000 9.201 < 2e-16 ***
## sex1 -0.2271 0.2188 278.8570 -1.038 0.3
## measurement1:sex1 1.8896 0.2828 196.0000 6.682 2.39e-10 ***
## measurement2:sex1 4.1677 0.2828 196.0000 14.738 < 2e-16 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr) msrmn1 msrmn2 sex1 msr1:1
## measuremnt1 -0.646
## measuremnt2 -0.646 0.500
## sex1 -0.707 0.457 0.457
## msrmnt1:sx1 0.457 -0.707 -0.354 -0.646
## msrmnt2:sx1 0.457 -0.354 -0.707 -0.646 0.500
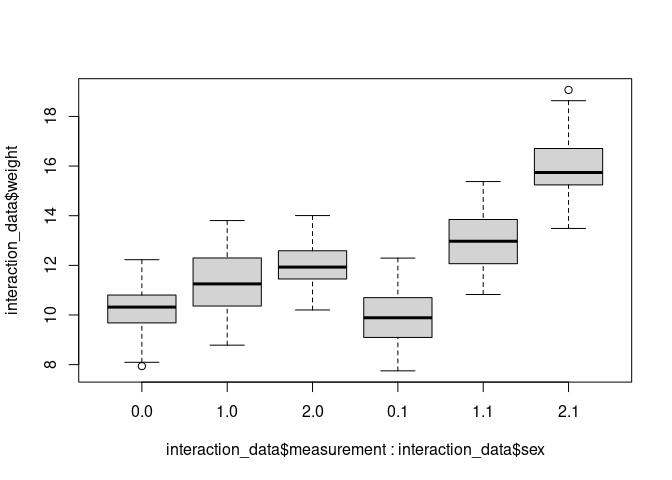
boxplot(interaction_data$weight ~ interaction_data$measurement * interaction_data$sex)
library(ggplot2)
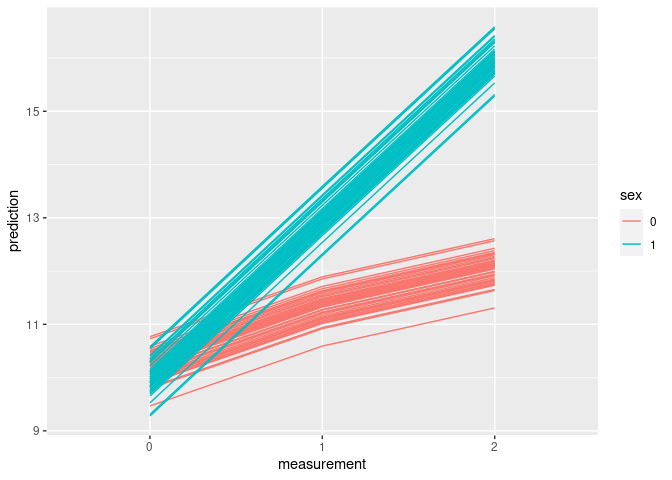
interaction_data$prediction <- unname(predict(model))
ggplot(interaction_data) + aes(x=measurement, y=prediction, group=id, color=sex) + geom_line()
Real data (cars)
library(tidyverse)
library(readxl)
car_data <-read_xls('data/kuiper.xls')
colnames(car_data)
## [1] "Price" "Mileage" "Make" "Model" "Trim" "Type"
## [7] "Cylinder" "Liter" "Doors" "Cruise" "Sound" "Leather"
car_data$Price <-scale(car_data$Price)
car_data$Mileage <-scale(car_data$Mileage)
car_model <- lmer(Price ~ Mileage + (1|Make), data = car_data)
summary(car_model)
## Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [
## lmerModLmerTest]
## Formula: Price ~ Mileage + (1 | Make)
## Data: car_data
##
## REML criterion at convergence: 1448.2
##
## Scaled residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.0336 -0.5711 -0.1192 0.2638 4.9021
##
## Random effects:
## Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
## Make (Intercept) 1.0387 1.0191
## Residual 0.3379 0.5813
## Number of obs: 804, groups: Make, 6
##
## Fixed effects:
## Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 0.20404 0.41674 4.99449 0.490 0.645
## Mileage -0.14175 0.02057 797.02317 -6.891 1.13e-11 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Correlation of Fixed Effects:
## (Intr)
## Mileage -0.001
Vik 2013, Chapter 18 (Repeated measures ANOVA)
In this chapter, the author performs a repeated measures ANOVA using an idiosyncratic calculation method. Here, I run the same analysis using the rstatix and car packages to show that the numbers correspond to what he calculates.
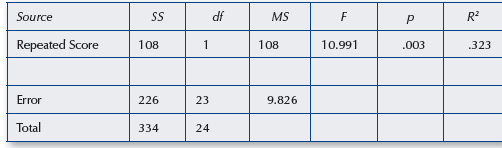
Vik, P. (2013). Regression, ANOVA, and the General Linear Model. SAGE Publications, Inc. (US). https://bookshelf.vitalsource.com/books/9781483316017
vik_data <- read_xls('data/vik_repeated.xls')
vik_data <- pivot_longer(vik_data, cols = c('time1', 'time2'))
head(vik_data)
## # A tibble: 6 × 3
## id name value
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 1 time1 3
## 2 1 time2 5
## 3 2 time1 5
## 4 2 time2 4
## 5 3 time1 6
## 6 3 time2 4
library(rstatix)
##
## Attaching package: 'rstatix'
## The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
##
## filter
res.aov <- anova_test(data = vik_data, dv = value, wid = id, within = name)
get_anova_table(res.aov)
## ANOVA Table (type III tests)
##
## Effect DFn DFd F p p<.05 ges
## 1 name 1 23 10.991 0.003 * 0.056
Here, the same thing using a different package that also spits out the sums of squares.
library(car)
## Loading required package: carData
##
## Attaching package: 'car'
## The following object is masked from 'package:dplyr':
##
## recode
## The following object is masked from 'package:purrr':
##
## some
design <- factorial_design(vik_data, dv = value, wid = id, within = name)
res.anova <- Anova(design$model, idata = design$idata, idesign = design$idesign, type = 3)
summary(res.anova)
##
## Type III Repeated Measures MANOVA Tests:
##
## ------------------------------------------
##
## Term: (Intercept)
##
## Response transformation matrix:
## (Intercept)
## time1 1
## time2 1
##
## Sum of squares and products for the hypothesis:
## (Intercept)
## (Intercept) 12696
##
## Multivariate Tests: (Intercept)
## Df test stat approx F num Df den Df Pr(>F)
## Pillai 1 0.798893 91.36671 1 23 1.7793e-09 ***
## Wilks 1 0.201107 91.36671 1 23 1.7793e-09 ***
## Hotelling-Lawley 1 3.972466 91.36671 1 23 1.7793e-09 ***
## Roy 1 3.972466 91.36671 1 23 1.7793e-09 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## ------------------------------------------
##
## Term: name
##
## Response transformation matrix:
## name1
## time1 1
## time2 -1
##
## Sum of squares and products for the hypothesis:
## name1
## name1 216
##
## Multivariate Tests: name
## Df test stat approx F num Df den Df Pr(>F)
## Pillai 1 0.3233533 10.99115 1 23 0.003017 **
## Wilks 1 0.6766467 10.99115 1 23 0.003017 **
## Hotelling-Lawley 1 0.4778761 10.99115 1 23 0.003017 **
## Roy 1 0.4778761 10.99115 1 23 0.003017 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Univariate Type III Repeated-Measures ANOVA Assuming Sphericity
##
## Sum Sq num Df Error SS den Df F value Pr(>F)
## (Intercept) 6348 1 1598 23 91.367 1.779e-09 ***
## name 108 1 226 23 10.991 0.003017 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1